Tensile strength is a critical property of materials. It determines their ability to withstand stretching forces without breaking. Engineers, manufacturers, and researchers rely on tensile strength measurements to ensure the durability, reliability, and safety of materials used in various applications, from construction and automotive industries to medical devices and aerospace engineering.
What is Tensile Strength?
In this article, we will delve into the concept of tensile strength, why it is important, and the various methods used to measure it accurately. Tensile strength is an important measurement. It is referred to as ultimate tensile strength, Its maximum stress that a material can endure while being stretched or pulled before breaking. It is expressed in units of force per unit area, commonly in megapascals (MPa) or pounds per square inch (psi).
This is an essential mechanical property that provides insights into the behavior of materials under tensile loads. This property is crucial in industries where materials are subjected to stretching forces, such as bridges, suspension cables, and machine components.
How to Measure Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is measured in a machine called a Universal Testing Machine. First, the material is placed into the testing machine and held on both ends using grips or clamps. Once in place, the machine will pull the material until it breaks. Throughout the test, the machine records the tension applied. Once the test is complete, the tensile strength is calculated by taking the maximum force and dividing it by the cross-sectional area.
With labels, tensile strength is measured in two directions: machine direction (MD) and transverse direction (TD). This is because some materials perform differently at different orientations.
Methods to Measure Tensile Strength
The tensile strength measured using standardized testing methods. The most common method is the Tensile Test, which follows standardized procedures set by organizations such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization).
1. Tensile Testing Machine (Universal Testing Machine – UTM)
A Universal Testing Machine (UTM) is used to perform tensile tests. This machine applies a controlled force to a specimen until it breaks, recording the stress-strain relationship throughout the process.
Steps to Conduct a Tensile Test
- Preparation of Specimen – A test sample is cut into a specific shape and dimensions according to ASTM or ISO standards.
- Mounting the Specimen – The sample is clamped between two jaws in the UTM.
- Applying Force – The machine pulls the specimen at a controlled rate.
- Recording Data – The machine measures the applied force and corresponding elongation.
- Breaking Point Analysis – Once the specimen breaks, the ultimate tensile strength is calculated using the recorded data.
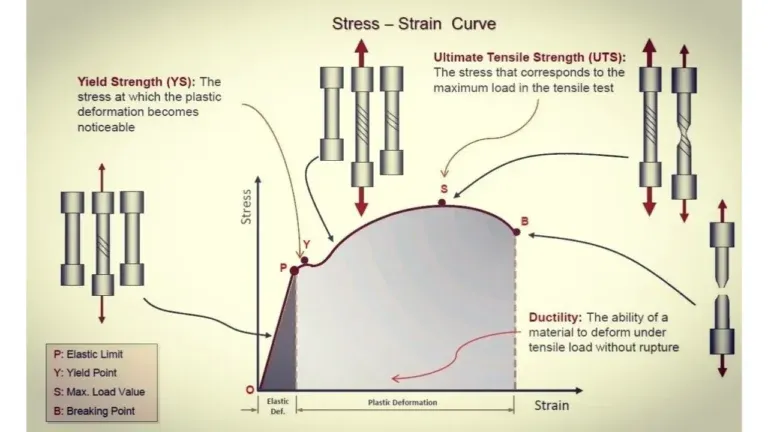
2. Stress-Strain Curve Analysis
During a tensile test, a stress-strain curve is generated. This curve provides insights into:
- Elastic region – Where the material deforms but returns to its original shape upon unloading.
- Plastic region – Where permanent deformation occurs.
- Fracture point – Where the material ultimately fails.
3. Non-Destructive Tensile Strength Testing Methods
While traditional tensile tests are destructive, some non-destructive techniques help estimate tensile strength without damaging the material:
- Hardness Testing – Indirectly correlates material hardness to tensile strength.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT) – Uses sound waves to detect material properties.
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD) – Determines internal stresses that relate to tensile strength.
- Acoustic Emission Testing – Monitors stress waves in materials under load.
4. Non-Destructive Tensile Strength Testing Methods
While traditional tensile tests are destructive, some non-destructive techniques help estimate tensile strength without damaging the material:
- Hardness Testing – Indirectly correlates material hardness to tensile strength.
- Ultrasonic Testing (UT) – Uses sound waves to detect material properties.
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD) – Determines internal stresses that relate to tensile strength.
- Acoustic Emission Testing – Monitors stress waves in materials under load.
Choose Top Tensile Structure in India
Tensile strength is important for understanding the structural integrity of materials. Through this process, manufacturers are able to accurately measure and assess the strength and durability of various components in order to ensure the safety and quality of their products. By becoming familiar with the mechanics behind tensile strength, manufacturers can gain invaluable insight into the durability of the materials.
Tensile Factory Pvt. Ltd. are the eminent organization involved in Manufacturing and Supplying a wide gamut of Tensile Structure. Also Read: Tensile Gazebo, Auditorium Tensile Structure, Tensile Car Parking and more. You can give us a call at +91-9911721005 or email us at tensilefactory02@gmail.com. Our team of technical experts will consult you regarding all your needs and queries.